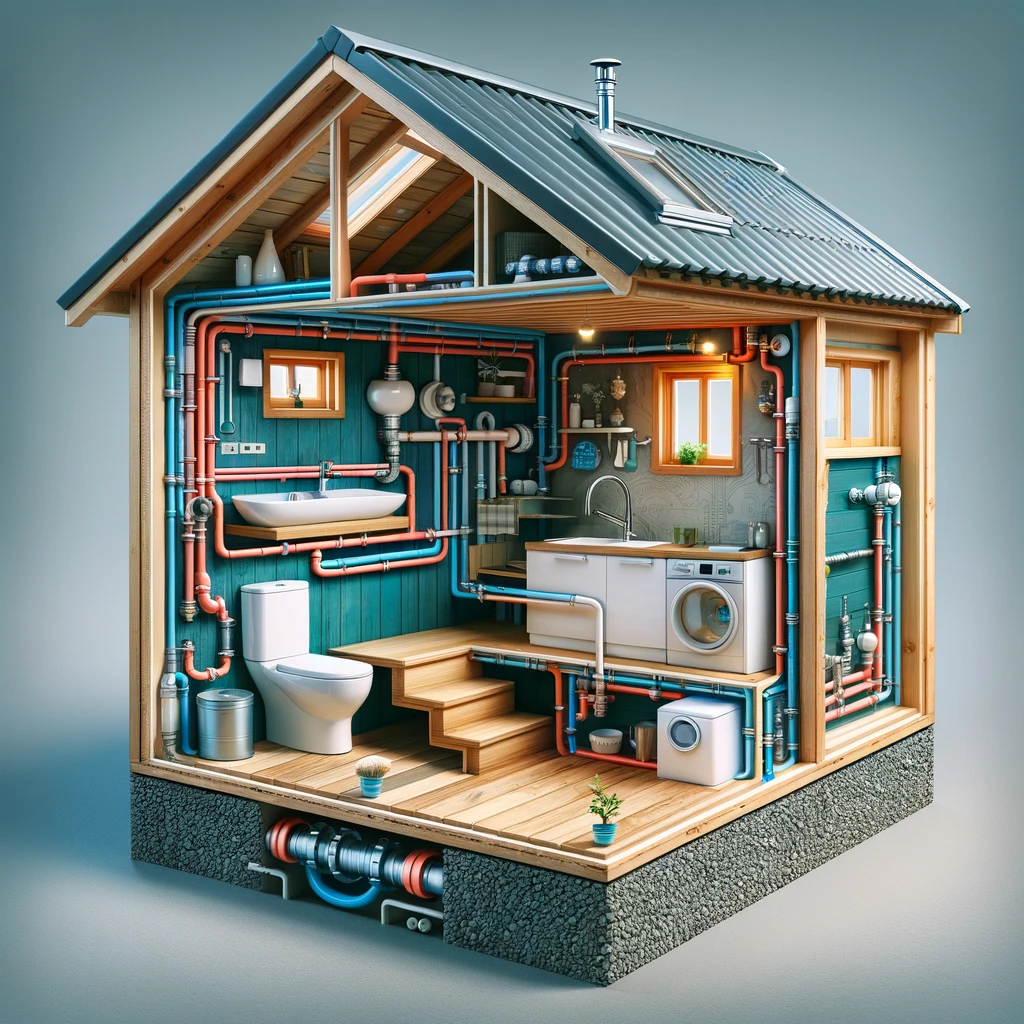

The growing popularity of tiny houses has sparked a revolution in residential design, emphasizing minimalism, efficiency, and sustainability. One of the crucial aspects of tiny house living is the plumbing system, which requires meticulous planning, innovative design, and careful consideration of expenses.
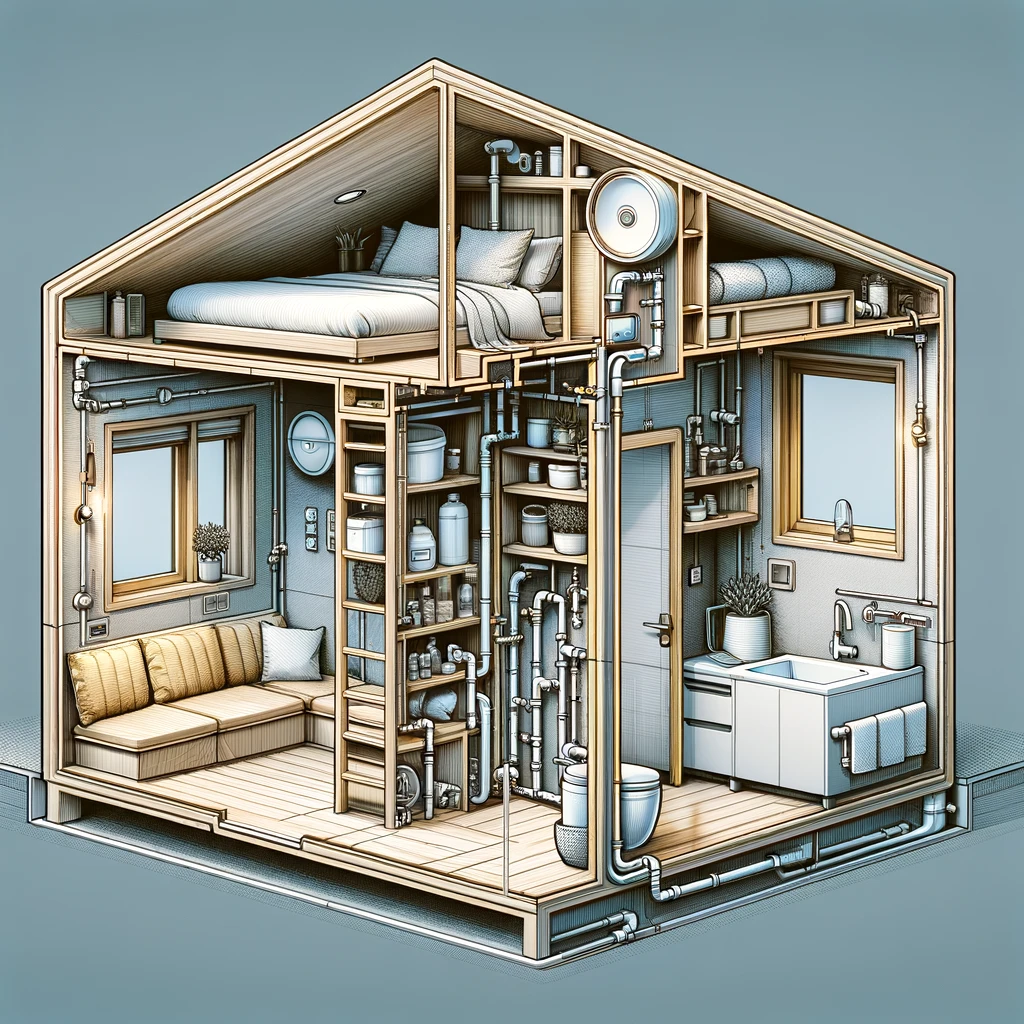
Planning the plumbing of a tiny house involves more than just installing pipes and fixtures; it necessitates a holistic approach to ensure the efficient use of space and resources. Given the limited square footage in a tiny house, every inch counts. The plumbing design must be compact and multifunctional. For instance, many tiny houses employ shower designs that also capture and reuse gray water for toilets or gardening, highlighting the importance of water conservation.
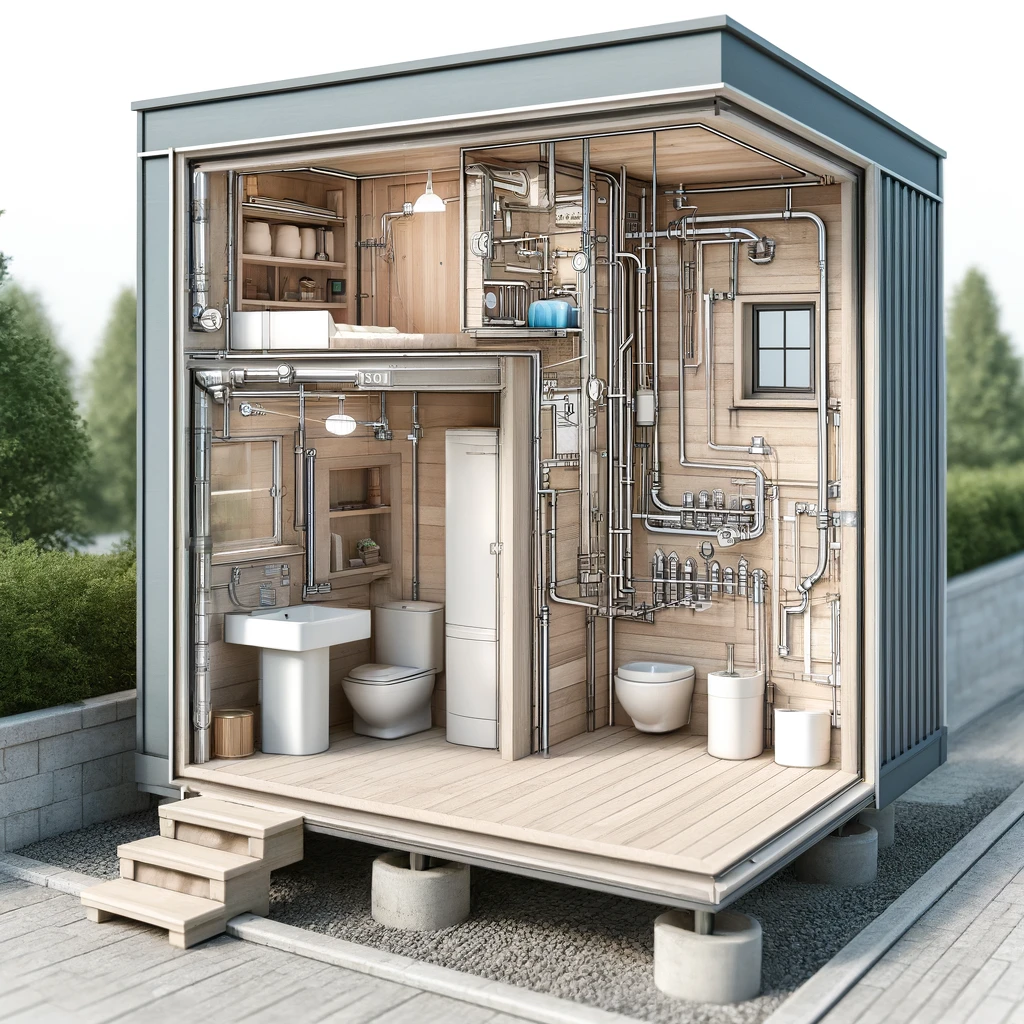

One of the most significant challenges in tiny house plumbing is managing water supply and waste. Unlike traditional homes, many tiny houses are not permanently connected to municipal water and sewer systems. Owners often rely on alternative water sources such as rainwater collection systems or portable water tanks, which must be meticulously designed to ensure a consistent and reliable water supply. Similarly, waste disposal solutions range from hooking up to public sewers where available, to more independent setups like composting toilets, which are favored for their low water usage and sustainability.
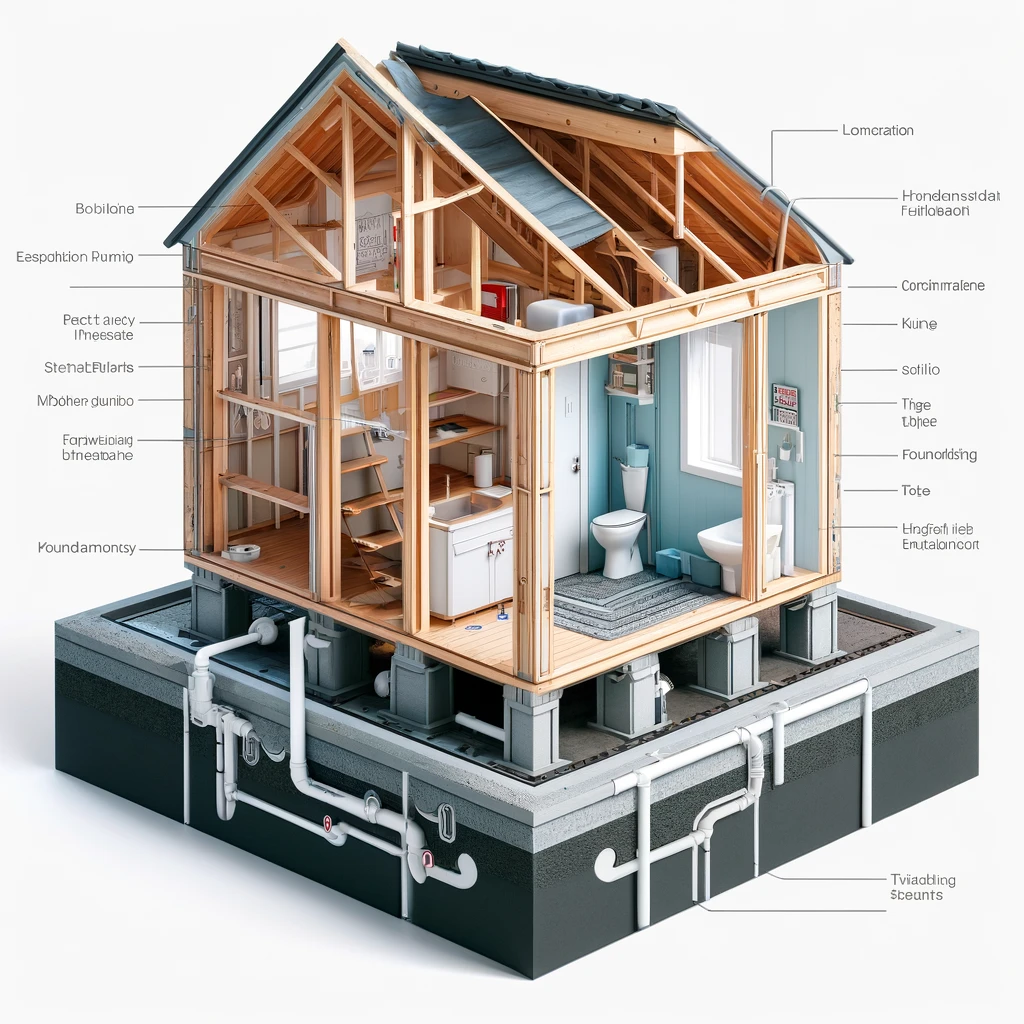
The design of plumbing systems in tiny houses also needs to consider the climatic conditions of the area. In colder climates, pipe insulation is critical to prevent freezing. The compact nature of tiny houses means that there is less buffer space inside the walls for plumbing, so additional protective measures may be necessary, such as heat tape or even re-routing pipes to run inside the living spaces where they are less likely to freeze.
Regarding expenses, the cost of plumbing a tiny house can vary widely based on the complexity of the system and the chosen technologies. For example, installing high-end fixtures, tankless water heaters, or high-tech composting toilets can increase costs but also contribute to the long-term sustainability and comfort of the home. Budgeting for plumbing in a tiny house is an exercise in balancing cost with functionality and environmental impact.
Investing in quality materials and professional installation can be cost-effective in the long run. While it might be tempting to cut corners, especially in a DIY project, skimping on plumbing can lead to costly repairs and maintenance issues down the line. Therefore, it is advisable to allocate a significant part of the budget to ensuring that the plumbing system is robust, leak-proof, and well insulated.
Additionally, tiny house owners must navigate various legalities, which can also impact the planning and expenses of plumbing systems. Zoning laws, building codes, and standards for water and sewage need careful consideration and can vary dramatically from one locality to another. Compliance with these regulations not only affects the initial design but also potentially involves fees and permits that add to the overall cost.
Plumbing in a tiny house requires innovative solutions that maximize space and efficiency. It involves careful planning to ensure that the system is sustainable, functional, and compliant with local regulations. While the upfront costs may be significant, especially with high-tech or eco-friendly systems, the long-term benefits of reduced water usage and lower living expenses can make these investments worthwhile. Thus, effective planning and design of plumbing systems are critical to the success and sustainability of tiny house living.
Tiny houses, showing the internal layout with a focus on the plumbing system.
Tiny houses, this time with a different layout that includes a compact bathroom and kitchen, showcasing the integrated plumbing system.
Tiny houses featuring a layout that includes a compact bedroom with a bed, along with the bathroom and kitchen, showcasing the integrated plumbing system.
Tiny house, this time focusing on the foundation and structural aspects, including how the plumbing system integrates with the base structure.